Collective action is essential for addressing the grand challenges of our time. However, for such action to be successful, decision-making processes must be perceived as legitimate. In this study, we investigate the legitimacy of different voting methods.
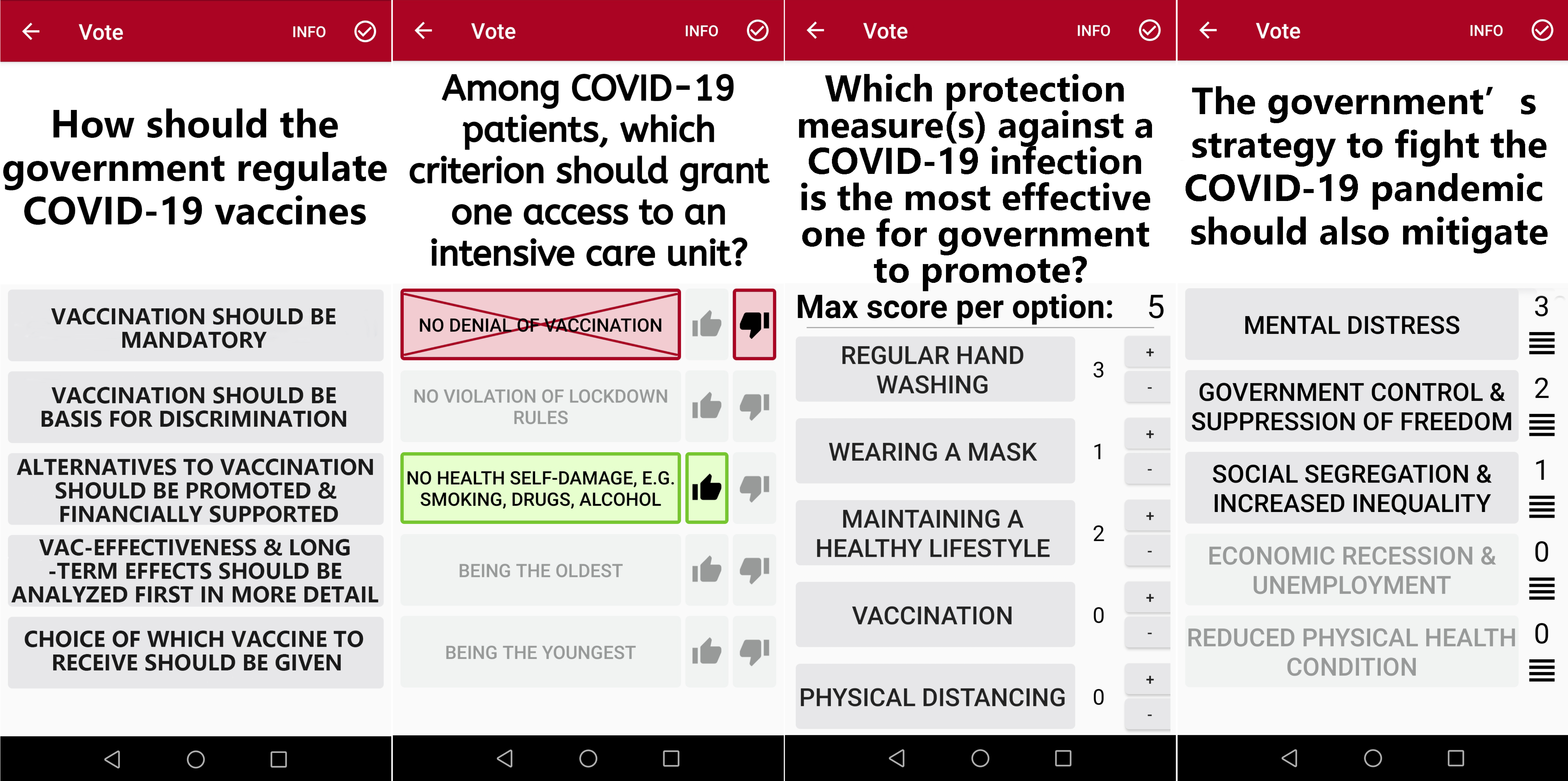 The participants voted upon 4 different questions via four different voting methods.
The participants voted upon 4 different questions via four different voting methods.
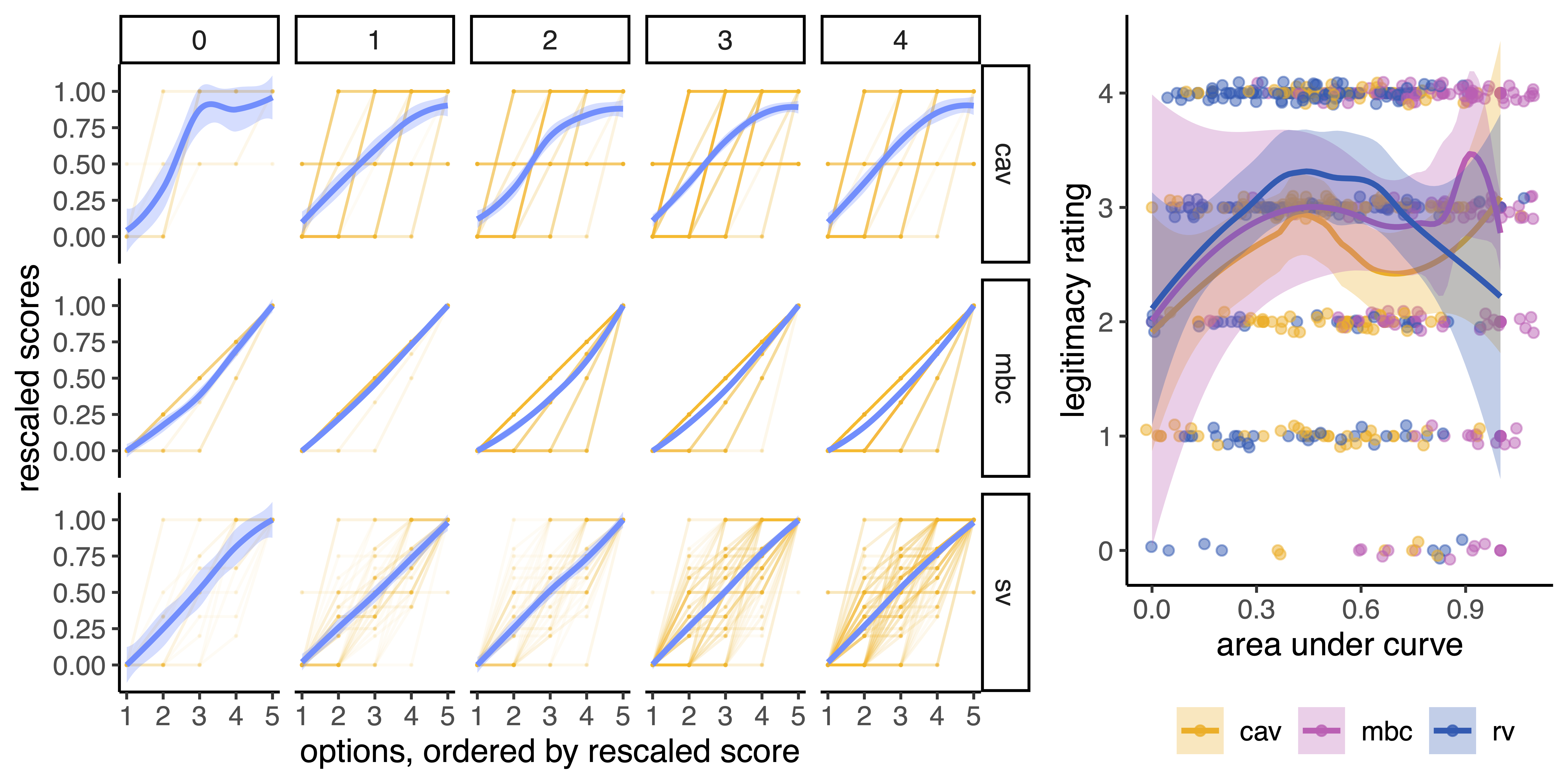
Using a pre-registered human subject experiment, 120 participants cast their votes using four voting methods: majority voting, combined approval voting, range voting, and modified Borda count. These methods represent a range of preference elicitation designs, from low to high complexity and flexibility. Furthermore, we developed a legitimacy scale upon which the participants rate the voting methods.
The experiment was conducted in a non-political setting (voting on color preferences) and a political context (voting on COVID-19-related questions). Our findings suggest that the perceived legitimacy of a voting method is context-dependent. Specifically, preferential voting methods are seen as more legitimate than majority voting in a political decision-making situation, but only for individuals with well-defined preferences. Furthermore, preferential voting methods are more legitimate than majority voting in a highly polarized situation.
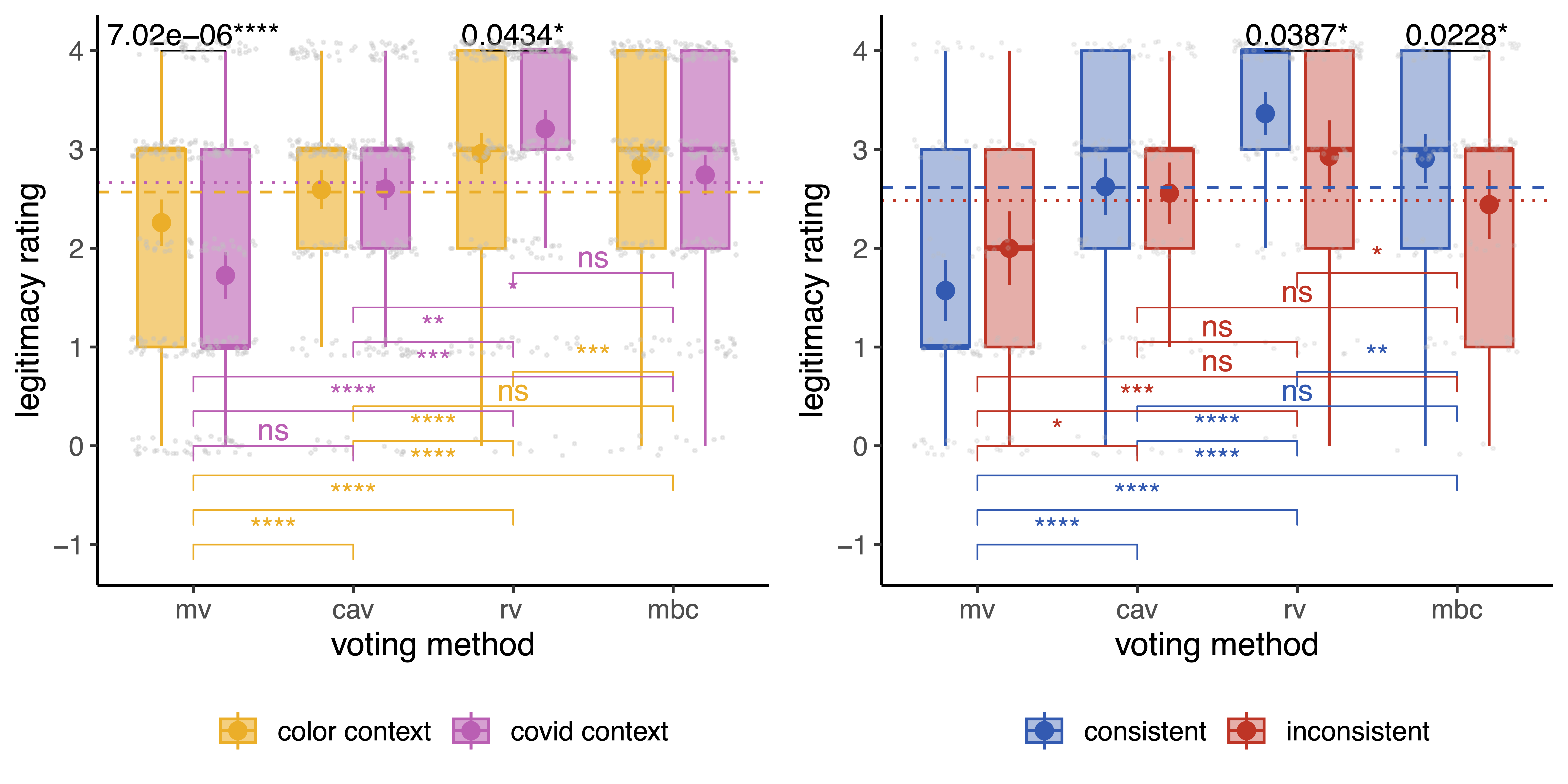 The perceived legitimacy of a voting method varies by context.
The perceived legitimacy of a voting method varies by context.
Citation
Link to our paper: How voting rules impact legitimacy
Hausladen CI, Hänggli Fricker R, Helbing D, Kunz R, Wang J, Pournaras E. How voting rules impact legitimacy. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications. 2024 May 29;11(1):1-0.